In recent years, silicon carbide compound semiconductors have received widespread attention in the industry. However, as a high-performance material, silicon carbide is only a small part of electronic devices (diodes, power devices). It can also be used as abrasives, cutting materials, structural materials, optical materials, catalyst carriers, and more. Today, we mainly introduce silicon carbide ceramics, which have the advantages of chemical stability, high temperature resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion coefficient, low density, and high mechanical strength. They are widely used in fields such as chemical machinery, energy and environmental protection, semiconductors, metallurgy, national defense and military industry.
Silicon carbide (SiC) contains silicon and carbon, and is a typical multi type structural compound, mainly including two crystal forms: α – SiC (high-temperature stable type) and β – SiC (low-temperature stable type). There are more than 200 multi types in total, among which the 3C SiC of β – SiC and the 2H SiC, 4H SiC, 6H SiC, and 15R SiC of α – SiC are representative.
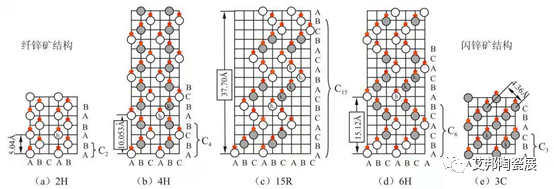
Figure SiC Multibody Structure
When the temperature is below 1600 ℃, SiC exists in the form of β – SiC and can be prepared from a simple mixture of silicon and carbon at around 1450 ℃. When the temperature exceeds 1600 ℃, β – SiC slowly transforms into various polymorphs of α – SiC. 4H SiC is easily generated at around 2000 ℃; Both 6H and 15R polymorphs require high temperatures above 2100 ℃ for easy formation; 6H SiC can remain very stable even at temperatures exceeding 2200 ℃, making it widely used in industrial applications.
Pure silicon carbide is a colorless and transparent crystal, while industrial silicon carbide can be colorless, pale yellow, light green, dark green, light blue, dark blue, or even black, with decreasing transparency levels. The abrasive industry categorizes silicon carbide into two types based on color: black silicon carbide and green silicon carbide. Colorless to dark green silicon carbide is classified as green silicon carbide, while light blue to black silicon carbide is classified as black silicon carbide. Black silicon carbide and green silicon carbide are both alpha SiC hexagonal crystals, and green silicon carbide micro powder is generally used as the raw material for silicon carbide ceramics.
Performance of Silicon Carbide Ceramics Prepared by Different Processes
However, silicon carbide ceramics have the disadvantage of low fracture toughness and high brittleness. Therefore, in recent years, composite ceramics based on silicon carbide ceramics, such as fiber (or whisker) reinforcement, heterogeneous particle dispersion strengthening, and gradient functional materials, have emerged successively, improving the toughness and strength of individual materials.
As a high-performance structural ceramic high-temperature material, silicon carbide ceramics have been increasingly applied in high-temperature kilns, steel metallurgy, petrochemicals, mechanical electronics, aerospace, energy and environmental protection, nuclear energy, automobiles and other fields.
In 2022, the market size of silicon carbide structural ceramics in China is expected to reach 18.2 billion yuan. With further expansion of application fields and downstream growth needs, it is estimated that the market size of silicon carbide structural ceramics will reach 29.6 billion yuan by 2025.
In the future, with the increasing penetration rate of new energy vehicles, energy, industry, communication and other fields, as well as the increasingly strict requirements for high-precision, high wear resistance, and high reliability mechanical components or electronic components in various fields, the market size of silicon carbide ceramic products is expected to continue to expand, among which new energy vehicles and photovoltaics are important development areas.
Silicon carbide ceramics are used in ceramic kilns due to their excellent high-temperature mechanical properties, fire resistance, and thermal shock resistance. Among them, roller kilns are mainly used for drying, sintering, and heat treatment of lithium-ion battery positive electrode materials, negative electrode materials, and electrolytes. Lithium battery positive and negative electrode materials are indispensable for new energy vehicles. Silicon carbide ceramic kiln furniture is a key component of kilns, which can improve kiln production capacity and significantly reduce energy consumption.
Silicon carbide ceramic products are also widely used in various automotive components. In addition, SiC devices are mainly used in PCUs (power control units, such as on-board DC/DC) and OBCs (charging units) of new energy vehicles. SiC devices can reduce the weight and volume of PCU equipment, reduce switch losses, and improve the working temperature and system efficiency of devices; It is also possible to increase the unit power level, simplify the circuit structure, improve power density, and increase charging speed during OBC charging. At present, many car companies around the world have used silicon carbide in multiple models, and the large-scale adoption of silicon carbide has become a trend.
When silicon carbide ceramics are used as key carrier materials in the production process of photovoltaic cells, the resulting products such as boat supports, boat boxes, and pipe fittings have good thermal stability, do not deform when used at high temperatures, and do not produce harmful pollutants. They can replace the commonly used quartz boat supports, boat boxes, and pipe fittings, and have significant cost advantages.
In addition, the market prospects for photovoltaic silicon carbide power devices are broad. SiC materials have lower on resistance, gate charge, and reverse recovery charge characteristics. Using SiC Mosfet or SiC Mosfet combined with SiC SBD photovoltaic inverters can increase conversion efficiency from 96% to over 99%, reduce energy loss by more than 50%, and increase equipment cycle life by 50 times.
The synthesis of silicon carbide ceramics can be traced back to the 1890s, when silicon carbide was mainly used for mechanical grinding materials and refractory materials. With the development of production technology, high-tech SiC products have been widely developed, and countries around the world are paying more attention to the industrialization of advanced ceramics. They are no longer satisfied with the preparation of traditional silicon carbide ceramics. Enterprises producing high-tech ceramics are developing more rapidly, especially in developed countries where this phenomenon is more significant. Foreign manufacturers mainly include Saint Gobain, 3M, CeramTec, IBIDEN, Schunk, Narita Group, Toto Corporation, CoorsTek, Kyocera, Aszac, Japan Jingke Ceramics Co., Ltd., Japan Special Ceramics Co., Ltd., IPS Ceramics, etc.
The development of silicon carbide in China was relatively late compared to developed countries such as Europe and America. Since the first industrial furnace for manufacturing SiC was built at the First Grinding Wheel Factory in June 1951, China began producing silicon carbide. Domestic manufacturers of silicon carbide ceramics are mainly concentrated in Weifang City, Shandong Province. According to professionals, this is because local coal mining enterprises are facing bankruptcy and seeking transformation. Some companies have introduced relevant equipment from Germany to start researching and producing silicon carbide. ZPC is one of the biggest manufacturer of reaction sintered silicon carbide.
Post time: Nov-09-2024