Silicon carbide and silicon nitride have poor wettability with molten metal. Besides being infiltrated by magnesium, nickel, chromium alloy and stainless steel, they have no wettability to other metals, so they have excellent corrosion resistance and are widely used in the aluminum electrolysis industry.
In this paper, the corrosion resistance of recrystallized silicon carbide R-SiC and silicon nitride bonded silicon carbide Si3N4-SiC in hot-circulating Al-Si alloy melts was investigated from multiple latitudes.
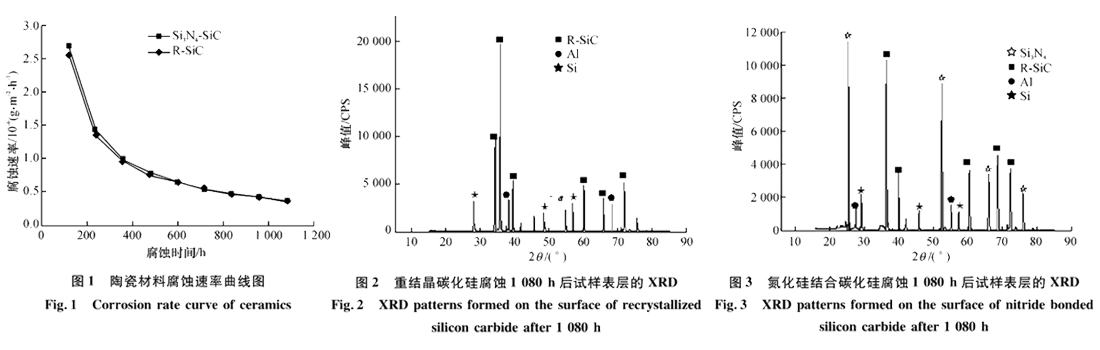
According to the experimental data of 9 times of thermal cycling of 1080h in 495 ° C ~ 620 ° C aluminum-silicon alloy melt, the following analysis results were obtained.
The R-SiC and Si3N4-SiC samples increased with corrosion time and the corrosion rate decreased. The corrosion rate accorded with the logarithmic relationship of attenuation. (figure 1)
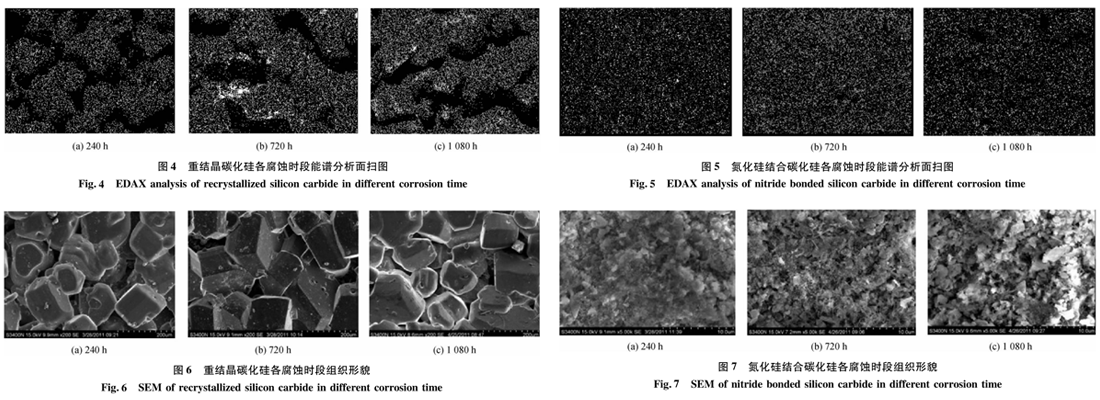
By energy spectrum analysis, the R-SiC and Si3N4-SiC samples themselves have no aluminum-silicon; in the XRD pattern, a certain amount of aluminum-silicon peak is the surface-residual aluminum-silicon alloy. (Figure 2 – Figure 5)
Through SEM analysis, as the corrosion time increases, the overall structure of R-SiC and Si3N4-SiC samples is loose, but no obvious damage. (Figure 6 – Figure 7)
The surface tension σs/l>σs/g of the interface between the aluminum liquid and the ceramic, the wetting angle θ between the interfaces is >90°, and the interface between the aluminum liquid and the sheet ceramic material is not wet.
Therefore, the R-SiC and Si3N4-SiC materials are excellent in corrosion resistance against aluminum silicon melt and have little difference. However, the cost of Si3N4-SiC materials is relatively low and has been successfully applied for many years.
Post time: Dec-17-2018